Introduction
By looking at the queries from the people about stock markets, we have decided to write an easy to follow ”Stock Investment for Dummies in 2024″. Entering the stock market is said to be among the most efficient types of investment that can create wealth in the long run. However, it could be off-putting for the first-time users due to the complexity and the aura of danger that accompanies it. This guide aims to simplify the process by focusing on two foundational investment vehicles, Index Funds and Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs). Also, this article will elaborate on the concept of Portfolio Allocation and why it is crucial along with proving how bonds and gold can be an inflation hedging tool.
What YOU Should Know
- Understanding Index Funds: Index funds are mutual funds designed to mirror the performance of a specific market index (e.g., S&P 500). They are cost-effective, provide diversification, and yield steady returns over the long term, making them ideal for passive investors.
- Popular Index Funds: Examples include Vanguard 500 Index Fund (VFIAX), Fidelity 500 Index Fund (FXAIX), and iShares Core S&P 500 ETF (IVV). These funds replicate the S&P 500 index and typically return 8-10% per annum, featuring low expense ratios.
- Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs): ETFs are investment funds traded like stocks on an exchange. They offer flexibility, diversification, and cost-effectiveness. Popular ETFs include Vanguard Total Stock Market ETF (VTI), Fidelity MSCI Information Technology Index ETF (FTEC), and iShares Core U.S. Aggregate Bond ETF (AGG).
- Portfolio Allocation: This involves dividing investments across various asset classes like equities, bonds, and cash to manage risk and achieve financial goals. It considers factors like age, risk tolerance, and investment horizon, ensuring a balanced and adaptive investment strategy.
- Hedge Against Inflation: Bonds (e.g., TIPS) and gold are used as hedges. Bonds provide fixed interest and mitigate stock market volatility, while gold maintains value during inflationary periods. Both assets offer diversification benefits, enhancing portfolio stability and long-term returns.
Index Funds: Stock Investment for Dummies
What are Index Funds?
Index funds are mutual funds that are created with the aim of mirroring the performance of a specific stock market index, be it the S&P 500 or the Nasdaq-100. While some investment funds try to achieve a higher return than the index, index funds simply mirror the index, so they are best for passive, long-term investors who want to minimize their investment expenses. [1]
Benefits of Index Funds
- Low Costs: Index funds usually have lower expense ratios relative to actively managed funds because there is no need to make constant trades.
- Diversification: An index fund gives you a broad market exposure and if one company or sector performs poorly, its impact is limited by being averaged out with other different kinds of investments.
- Steady Returns: In the long-run, index funds provide moderate and stable returns that are in line with the market performance. [2]
Example of popular index funds
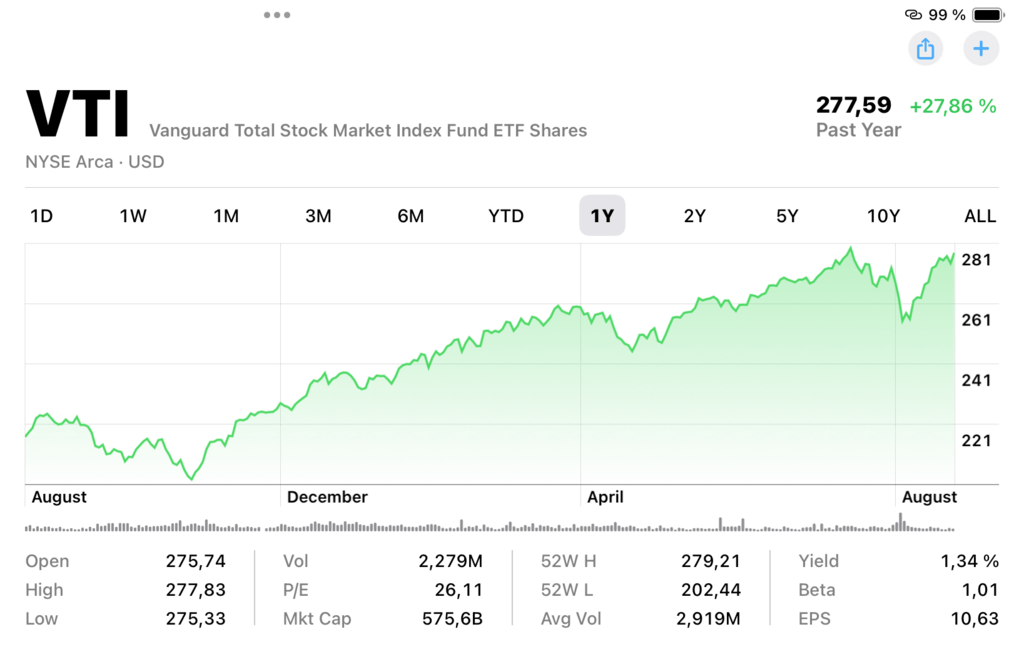
- Vanguard 500 Index Fund (VFIAX): The fund focuses on the index level S&P 500 which give investor an exposure to 500 large companies in the United States Equity Market. Despite its performance, it has been earning between 8-10% per annum on average in the last 20 years.
- Fidelity 500 Index Fund (FXAIX): Like the Vanguard 500 Index Fund, this Fidelity fund also follows the same S&P tracking index. It performs as well as other index funds with very low expense ratios, which is why it is suitable for long-term investment.
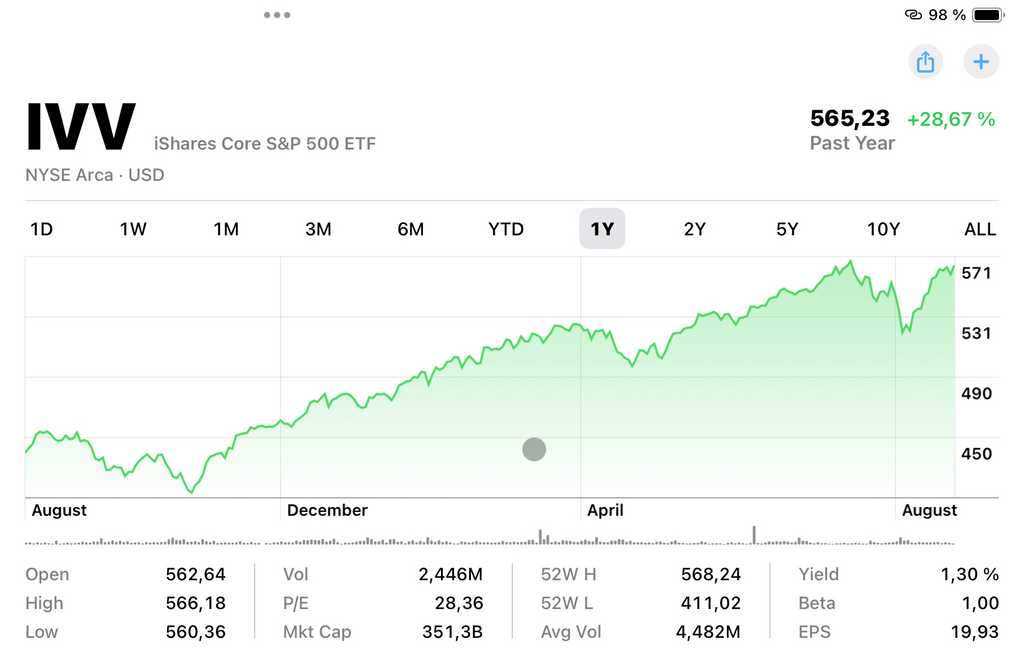
- iShares Core S&P 500 ETF (IVV): Like most of the ETFs, IVV functions more like a typical index fund though it tracks the S&P 500 index. It is characterized by low costs with high performance over a long period. [3]
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs)
What are ETFs?
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) are investment funds that are listed and traded on Stock Exchange Markets similar to individual stocks. It includes stocks, bonds, or commodities and intended to give investment results that correspond to the changes in the value of a specific index or group of industries. ETFs share some features with mutual funds but are tradable like individual stocks while providing diversification. [4]
Benefits of ETFs
- Flexibility: However, unlike mutual funds, which have their Net Asset Value calculated at the end of the day and can only be purchased at this price, ETFs can be sold and bought at the current market price during the whole trading session.
- Diversification: Like index funds, ETFs invest in many securities and, therefore, have built-in diversification inherent in the ETF structure.
- Cost-Effective: Most ETFs are fairly cost effective with their expense ratios, which means they would be perfect for a diversified investment. [5]
Examples of Popular ETFs
- Vanguard Total Stock Market ETF (VTI): It tracks the performance of the entire stock market of United States including the small cap, mid cap, large cap stocks. It is an all-inclusive solution for those interested in diversifying their portfolios and getting more exposure to a general market.
- Fidelity MSCI Information Technology Index ETF (FTEC): This is an index ETF that targets companies that operate within the technology industry and measures their performance against the MSCI USA IMI Information Technology Index.
- iShares Core U. S. Aggregate Bond ETF (AGG): This ETF give investors the opportunity to invest in the U. S. investment-grade bonds market and, as such, it can be perfectly suitable for those who want to diversify their portfolio with low-risk products and fixed-income instruments. [6]
Performance Review: Index Funds and ETFs
The growth of index tracking funds, for instance, Vanguard 500 Index Fund (VFIAX) and Exchange traded funds (ETFs) such as iShares Core S&P 500 ETF (IVV) over the past two decades has also been impressive with a yearly return rate of about 8-10%. This performance establishes that stock market investments in the United States remain stable and have the capacity to grow when held for some time.
This is where, through compounding, reinvested dividends and capital gains contribute to the exponential growth of investments’ value. This compounds the benefits, especially when considering that the fees for index funds and ETFs are relatively low, enabling investors to grow their wealth without the need to trade frequently or on a short-term basis. Learn Long term investing HERE!
Moreover, steady outcomes of such investment instruments also suggest the suitability of a long-term investment strategy, more specifically, investing and holding. This is because investors lack the impulses to act on daily and weekly turns in the market by purchasing stocks since in the long run the stock market tends to rise higher than other forms of investment such as inflation and other assets. They reduce the effect of market fluctuations since it is common to witness a decline in a given period followed by an improvement and growth. Consequently, investors who have the long-term orientation, will be able to achieve their investment objectives effectively, whether it is for saving for retirement, education or for any other purpose. [7]
Portfolio Allocation
What is Portfolio Allocation?

Asset allocation is the division of one’s investments across categories, including equities, fixed-income investment and cash instruments. The aim is to manage and divide risk and return based on an investor’s objectives, susceptibility to losing money, and investment timeframe. [8]
Importance of Portfolio Allocation
- Risk Management: Risk management is achieved through diversification of securities in the portfolio across various classes of assets. This decreases the effect of poor performance in any of the assets since they are dispersed across the various portfolios.
- Achieving Goals: Portfolio diversification is channel-specific and personalized to your saving needs, whether it is for retirement, home, or any other financial milestone.
- Adapting to Life Changes: It also allows for flexibility where changes may be made on the portfolio depending on the client’s age or changes in financial situation. [8]
How to Approach Asset Allocation
- By Age: One of the most widely accepted adages of investing for beginners is the percentage of your portfolio that stocks should make up, and that is 100 minus your age. For instance, the level of asset allocation might be 70% investments in stocks and 30% investments in bonds for a 30-year-old.
- By Risk Tolerance: Depending on this, you could invest more in stocks and bonds if your tolerance for risks is high because these investments are volatile but can bring significantly larger returns compared to bonds. On the other hand, if you are more conservative and do not want to take much risk, you would prefer more investments in bonds and cash.
- By Time Horizon: The longer the investment horizon one has, the more the percentage of one’s investment that can be invested in the more risky investments such as equities. When approaching your financial goals, it is wise to transition to safer investments such as bonds and gold to protect your money. [8]
Using Bonds and Gold as a Hedge against Inflation
Bonds
Bonds are a basic class of investments, which involve the lending of money to borrowers that includes governments, corporations, or other organizations in exchange of fixed interest and promise to pay back the face value of the bond at the time of its maturity.
While stocks refer to ownership in a given company, bonds are seen to be more secure in the sense that they give fixed coupon tones, unlike the fluctuating stock market returns, hence, appealing to the conservative investor or anyone holding near-retirement status. In addition, bonds have their maturity period wherein the holder of the bond gets the face value of the bond relieving the bondholder from being tangled in fluctuating stock prices unlike the stocks. [9]
When it comes to inflation, bonds have their disadvantage as inflation merely wears away the value of future receivables. However, some bonds like Treasury Inflation-Indexed Securities (TIPS) have been created with this problem in mind. TIPS are essentially a form of U. S. government bond in which the face value of the bond fluctuates with changes in the inflation rate as reflected by the CPI.
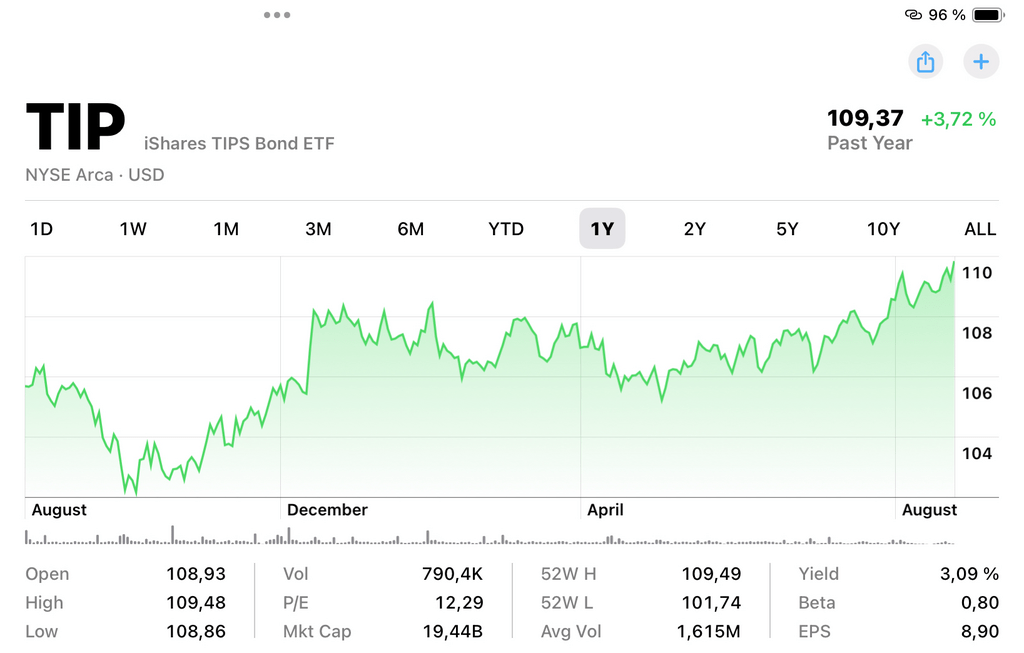
This adjustment is useful in ensuring the real value of bondholder’s investment is protected hence making TIPS important to investors when it comes to protection against inflation. Also, the use of bonds in an investment portfolio makes risk diversification easier as bonds are able to moderate the overall volatility of investment.
This type of investment tool is used to balance the portfolio and generally has an inverse performance measure in relation to stocks, so they are most attractive during the times when equities are worst performing. It also means that bonds can help investors to avoid the greatest fluctuations in income and experience a more stable multiple-year return on investment.
Gold
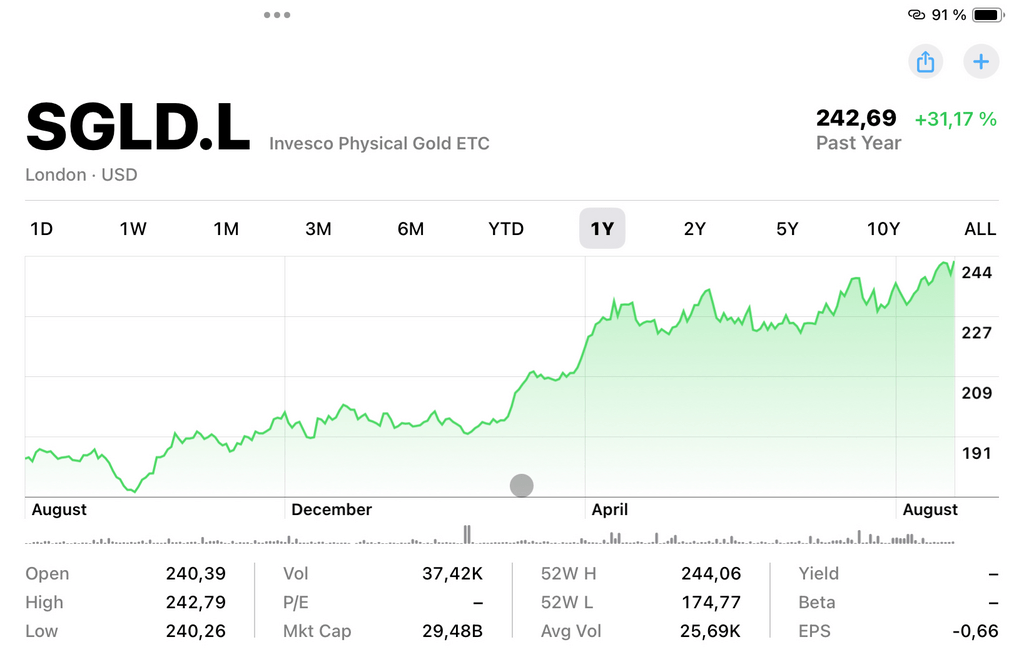
Gold has been used as a medium of exchange or a means of saving in the process that may last for thousands of years. It has become popular due to the fact that it helps people maintain their money, particularly in non-stable economies.
Gold is generally a store of value unlike paper money that in most cases is prone to inflation and therefore decreases in value. It has this characteristic that makes it an investors’ preference in hedge against the inflationary degradation of other assets. When inflation increases, the value of currency reduces while gold which is a kind of asset most of the time, gains value. This inverse relationship between gold and inflation is why many investors look towards gold as a hedge to lock their assets and not be harmed by increasing prices.
Gold as an inflation hedge is a well-documented fact, but what is often overlooked is the diversification advantage that it provides. Diversification is an important technique of investment, because it lessens the effects of poor investment on the overall investment portfolio.
Gold volatility or the movement in the price of gold does not move in harmony with stocks and bonds that is why at a time when stocks and bonds may be declining, gold may remain firm or even appreciate in value. Holding gold as part of a diversified investment strategy helps investors to reduce risks to their investments and possibly achieve better returns in the long run. This attribute of gold insurance makes it most useful in bear markets, and therefore, must form an important part of a well-diversified and secure portfolio. [10]
Conclusion
Purchasing index funds and ETFs is the simplest and cheapest method of attaining exposure to long-term stock market gains. If you distribute your portfolio over different classes of assets and include bonds and gold as inflation hedges in your investment plan, you will be able to achieve a diversified approach to risk management. Lastly, investing is primarily a patience affair and long-term game that requires strong determination and perseverance. You can accumulate wealth and achieve your goals, therefore, it is important to always take the correct approach.