Introduction: Solid Performance Amid Turbulent Tides
For the first quarter, Nvidia earnings Q1 2026, which Nvidia reported on May 28, 2025, AI and data center strength propelled their results once again. Compared to the previous year, revenue increased by 69% for a total of $44.1 billion, and the company also made $18.775 billion in net income (Nvidia, 2025a). Even with a huge $4.5 billion loss on H20 chips because of new U.S. export limits to China, the company managed to grow. These arrangements, especially with Humain and G42, point to a strong effort to join the emerging AI market in the region (FT, 2025a).
Nvidia Earnings Q1 2026: Momentum Continues
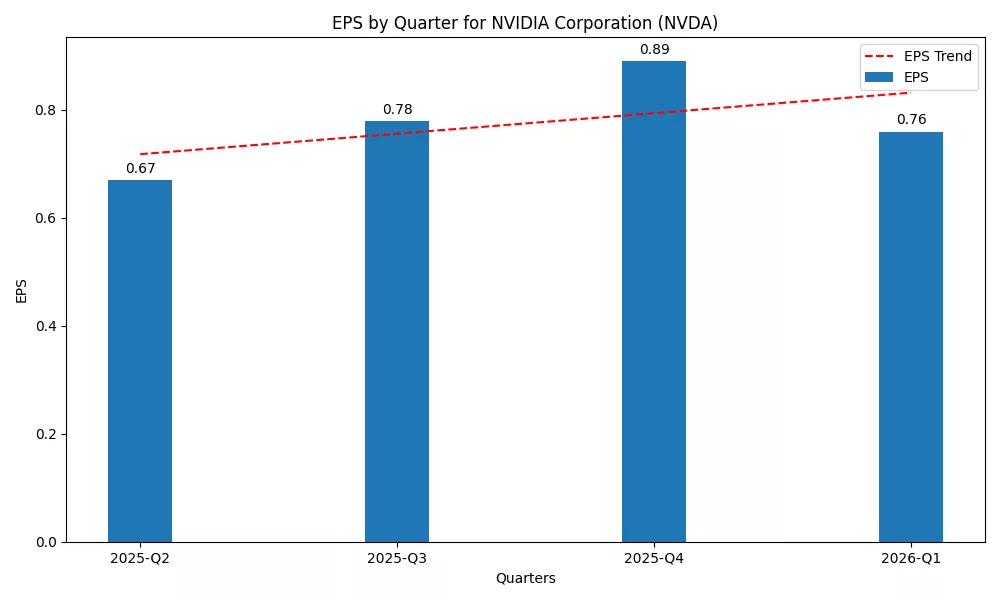
Revenue and EPS
For Q1 2026, Nvidia earned $44.1 billion, with most of the revenue, or $39.1 billion, coming from the Data Center business segment. Gaming brought in $3.8 billion, and Automotive and Robotics contributed $567 million. Even after including the H20 chip charge, Nvidia achieved $0.76 in diluted EPS, but it was $0.96, excluding the charge (Nvidia, 2025a).
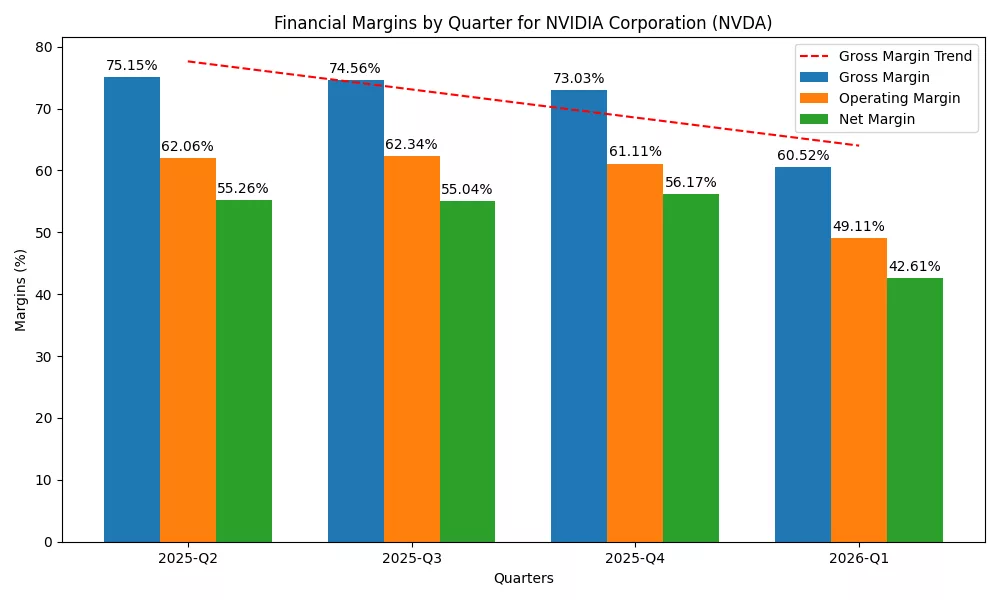
Margins
Despite the H20 charge cutting the gross margin to 60.5%, it rose to 71.3% once adjusted, demonstrating how Nvidia still makes good profits (Nvidia, 2025a). Trade disruptions playing a role now led companies to report earnings in the 70–71% margin range.
Key Segments Analysis
Data Center
Nvidia’s Data Center segment generated 89% of the company’s revenue due to growing interest in large language models (LLMs), recommendation engines, and generative AI applications (Nvidia, 2025a). More and more big clients, cloud services, and new AI companies are using the Blackwell GPU architecture.
Gaming
Gaming revenue hit $3.8 billion, reflecting Nvidia’s performance in meeting demand with its powerful RTX graphics cards and popular gaming laptops. It supports the brand and provides acceptable margins, as discussed by Nvidia (2025a).
Automotive & Robotics
The autonomous vehicles and robotics segment brought in $567 million because of Nvidia’s advanced work with Jetson and DRIVE (Nvidia, 2025a).
China Restrictions and the H20 Write-Off
On April 9, 2025, exports of Nvidia’s H20 chips and similar high-end integrated circuits going to China, Hong Kong, and Macau were made subject to tough export license policies by the U.S. government. As a consequence, Nvidia faced a charge of about $4.5 billion in Q1 FY2026 for left-over inventory and agreements with suppliers (Nvidia, 2025a). Before the ban, the company earned $4.6 billion from H20 chips during the quarter, showing there was strong demand at that time.
Nvidia plans to write off around $8 billion in China, which used to play a key role in their AI hardware growth and is expected to reach $50 billion soon (FT 2025b). The effects are very important:
- Chinese players are now more likely to take over Nvidia’s spot in China’s data center market, which could be permanent.
- Because of the ban, gross margins decreased by almost 11 points, falling to 60.5% from 71.3%.
- The potential of future products for success in China is not certain because U.S. export controls keep evolving.
Nvidia must now find new solutions or partner with more suppliers outside the West.
Global Strategic Pivot: Middle East AI Ambitions
Due to increasing policies and disputes from China and the U.S., Nvidia is concentrating on stepping up its global presence, especially in the Middle East. Two important contracts have brought the company to the forefront of AI change in the region.
In Saudi Arabia, Nvidia has joined forces with Humain to help make AI factories, supporting the efforts to adjust from being oil-based to being supported by technology (FT, 2025a). Local AI development, protecting digital sovereignty, and a greater need for Nvidia’s chips across health, energy, and education are the main goals for these factories.
The UAE’s Nvidia is partnering with G42, an important AI company, to create the largest AI infrastructure project anyone has ever built in the area. This will mean setting up Nvidia’s data center architecture, from the GPUs right through to the various enterprise software layers (FT, 2025a).
These actions, in combination, show that Russia wants to reduce its dependence on the US-led system. They give Nvidia the chance to join active AI initiatives in China, control China-related risk, and build its status as a leading brand in rising digital economies that can invest heavily. If you would like to compare the results to previous quarter here is the link: Nvidia Earnings Q4 2024 Analysis: Is it a buy in 2025?
Summary Table: Nvidia Earnings Q1 FY2026 Highlights
| Metric | Value | Notes |
| Total Revenue | $44.1 billion | Up 69% YoY |
| Data Center Revenue | $39.1 billion | 89% of total revenue |
| Gaming Revenue | $3.8 billion | Solid performance amid AI focus |
| Automotive & Robotics Revenue | $567 million | Growth driven by autonomous & robotics platforms |
| Net Income | $18.775 billion | Affected by $4.5B H20 write-down |
| Gross Margin (incl. charge) | 60.5% | Due to H20 chip write-off |
| Gross Margin (excl. charge) | 71.3% | Core profitability remains strong |
| Diluted EPS (incl. charge) | $0.76 | Reflects the impact of export restrictions |
| Diluted EPS (excl. charge) | $0.96 | Underlying earnings potential |
| H20 Chip Write-Off | $4.5 billion | Triggered by the U.S. export ban to China (April 2025) |
Investor Takeaways: Is Nvidia a Good Stock to Buy?
Q1 2026 earnings for Nvidia prove that the company swiftly deals with worldwide unrest. Investors see many strong reasons to invest in startups.
- Leadership in AI hardware: Because Nvidia’s GPUs, such as the Blackwell, are leading the way, there will always be a steady demand for their products both in the cloud, business, and government worlds.
- Geographic Pivot: Collaborations with Saudi Arabia and the UAE help bring in more money and widen Antofagasta’s business reach.
- Financial Strength: Nvidia demonstrated resilience last year by still having solid margins (71.3%) and $18.775 billion net earnings, even with the China incident.
At the same time, there are still some risks:
- Geopolitical Fragility: Continued uncertainties between the U.S. and China in the tech sector could lead to more export restrictions, which could stop growth.
- Valuation Concerns: Nvidia’s price is very high, with a higher P/E than peers, so it can be affected by shifts in the market.
- Open-Source Threats: Rising use of open-source AI models could make Nvidia’s proprietary CUDA less important.
Conditions largely support Nvidia as a strong long-term investment in AI, but investing comes with the challenge of looking closely at all other uncertainties and issues, mainly from plans to write down $8 billion in China due to concerns of a slowing market.
Conclusion
In Q1 2026, the company performed strongly, even as complexities in the industry kept growing. Revenue of $44.1 billion and continued leadership in data center AI and computer show that Nvidia is fulfilling its long-term strategy. How quickly geopolitical risk becomes a financial issue is clearly demonstrated by the $4.5 billion H20 chip charge. Even so, the company’s shift towards the Middle East, advanced technology, and steady customer base provides potential upside in the long run, which makes it attractive for AI specialists, although with caution.
Disclaimer
The content provided herein is for informational purposes only and should not be construed as financial, investment, or other professional advice. It does not constitute a recommendation or an offer to buy or sell any financial instruments. The company accepts no responsibility for any loss or damage incurred as a result of reliance on the information provided. We strongly encourage consulting with a qualified financial advisor before making any investment decisions.