Is Apple stock worth buying in 2026 after AI and services growth? A valuation-driven look at risks, expectations, and long-term returns.
Apple Stock Analysis 2026: Opportunity or Risk?
Apple stands in an opportune place in its company and market history as we enter the year 2026. The company is now registering a quantifiable revenue strength after several years of macroeconomic variation, supply chain realignments and the changing consumer demand behaviour. The iPhone sales are once again registering a considerable improvement, Services revenue is steadily growing, and artificial intelligence characteristics are being interwoven throughout devices and software platforms. All these developments are an indication of the momentum of operations and not stagnation.
Nevertheless, good performance by itself is not a sufficient condition for investment. The financial markets do not value the historical successes but the prospects. We examined this expectation gap in detail in our analysis of market psychology versus financial reality, “analysis of market psychology versus financial reality“. This is why investors are posing a tough question as opposed to acting emotionally:
Is Apple stock a buy in 2026, or are the growth prospects already embedded in the present valuation?
This is not a question of whether Apple is a quality company or not. The question is: can the future growth of Apple, especially due to the integration of AI, as well as an increase in the revenue of services, retain the levels of valuation implied by the current market price?
To respond to this accurately, the analysis will need to go beyond the headlines and only concentrate on financial structure and growth sensitivity. This article will justify the reason of worth to buy Apple stock in 2026, after AI and Services Growth, or Is it a Trap?
For a deeper long-term valuation breakdown extending through 2030, see our detailed intrinsic value model and expected return scenarios, “intrinsic value model and expected return scenarios.“
Table 1: Intrinsic Value Sensitivity (Based on Long-Term Growth)
| Long-Term Growth Rate | Estimated Intrinsic Price ($) |
| 2% | 112 |
| 3% | 128 |
| 4% | 149 |
| 5% | 178 |
| 6% | 220 |
| 7% | 292 |
The assumptions of long-term growth are highly sensitive when it comes to Apple’s stock valuation analysis.
- 2-3 % GDP growth produces an intrinsic value of between $ 112 and $128.
- Valuation boosts at 5% or 6% growth.
- Valuation is aggressive at a 7% growth.
Therefore, before asking the question of whether to buy Apple stock, investors need to determine a realistic growth rate.
Portfolio Analysis: How Apple Fits in a Long-Term Strategy
Growth Portfolio Perspective (High Risk / High Return)
A growth portfolio is intended to be used by investors who want to achieve high capital growth in the long run. Stability and income are not the main goals, but the growth of price in the long run is driven by earnings expansion.
The investors of growth portfolios usually:
- Tolerate short-term volatility.
- Target revenue acceleration.
- Focus on innovation and scalability.
- Comfortable with valuation risk.
Apple will only be appealing when investors have the belief that AI integration and Services growth will be able to support more significant growth in the long run (approximately 5-6% or more). Then intrinsic value has expansive potential, provided upside growth potential.
But there is a risk of the sensitivity of the above explained expectations. Valuation compression may hold returns down in case the growth decelerates to 2 to 3% though less likely. Thus, Apple in a growth portfolio is not so much about safety, as sustainable expansion is fueled by innovation.
Balanced Portfolio Perspective (Moderate Risk / Reward)
A balanced portfolio tries to work out growth potential and capital stability. The goal will be to attain above average expected returns from Apple stock and lessen extreme volatility.
Balanced investors normally:
- Divest in growth and stable assets.
- Seek moderate appreciation
- Emphasize the durability of earnings.
- Risk averse to too much concentration.
On a balanced view, Apple suits well, given its revenue base that is diversified and recurring Services income. The company has a moderate growth with no high-risk profile that comes with smaller technology companies.
If Apple continues growing at 4-5% long run, that fits the goal of a balanced portfolio very well. Our long-term growth framework through 2030 explores how sustainable expansion impacts valuation over multiple market cycles, “long-term growth framework through 2030“. Nevertheless, excessive exposure or unrealistic growth expectations may add extra volatility in it. Thus, disciplined position sizing tends to play a role in this context.
Conservative Portfolio Perspective (Low Risk / Capital Preservation)
A conservative portfolio is one that lays emphasis on stability, reliability of income and capital protection as opposed to aggressive growth. This is aimed at reducing downside risk.
Conservative investors usually:
- Prefer already existing mega-cap firms.
- Appreciate predictable cash flows.
- Pay attention to financial resilience.
- Evade speculative assets
Structural strength comes in the form of global diversification and ecosystem lock-in of Apple. It has recurring Services revenue, which gives it a stabilising factor as opposed to pure hardware businesses.
Conservative investors are, however, advised to be careful of valuation, as the current valuation is high offering less to no margin of safety. Downside risk goes up when the stock price is assumed to grow aggressively in the long run. Apple would suit only the preservation of capital strategy as long as the growth assumptions are realistic and the margin is maintained.
Table2: Comparison among portfolios
| Portfolio Type | Risk Level | Main Objective | Apple’s Role |
| Growth | Low | Capital appreciation | Innovation-driven compounder |
| Balanced | Moderate | Steady growth + stability | Core allocation with moderate expansion |
| Conservative | High | Capital preservation | Stable mega-cap but current valuation is high |
Geographic Diversification: Structural Strength
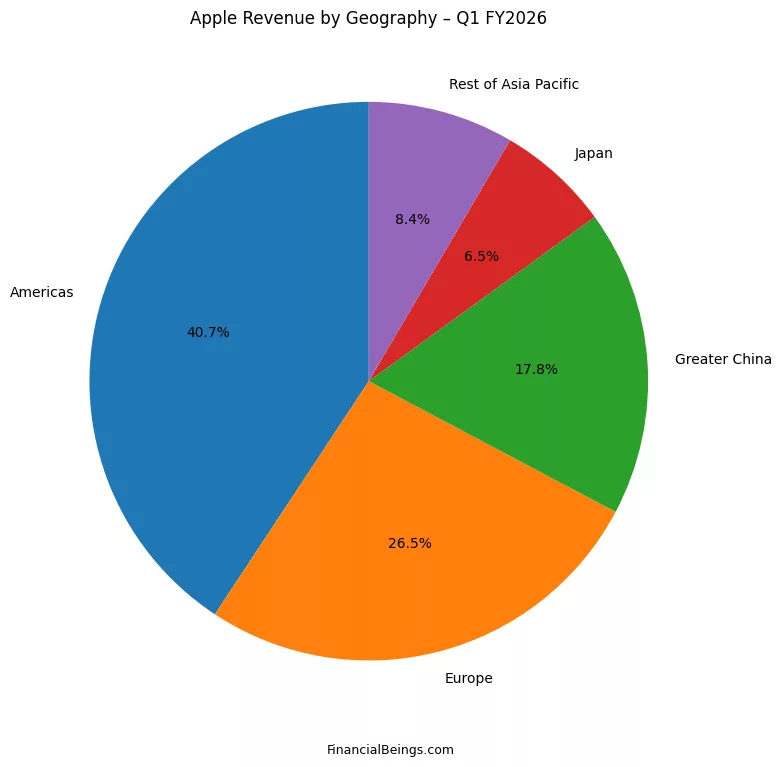
Table 3: Revenue by Geography – Q1 FY2026
| Region | Revenue Share |
| Americas | 40.7% |
| Europe | 26.5% |
| Greater China | 17.8% |
| Japan | 6.5% |
| Rest of Asia Pac | 8.4% |
The Americas is the major revenue generator at 40.7%, with Europe at 26.5%. Greater China is also strategic yet not dominant, with a contribution of 17.8%, however the slower China sales hit the stock valuation recently due to fears of slower demand hampering revenue.
This distribution indicates that Apple is not over-reliant on one country. Structural risk is minimized by geographic diversification, and it promotes stability but risk remains (Yahoo Finance, 2026; Financial Times, 2026).
The point of stability makes the argument stronger in asking again: Is the Apple stock worth buying for a long-term portfolio ?
Product Revenue Breakdown: Where Growth Is Concentrated
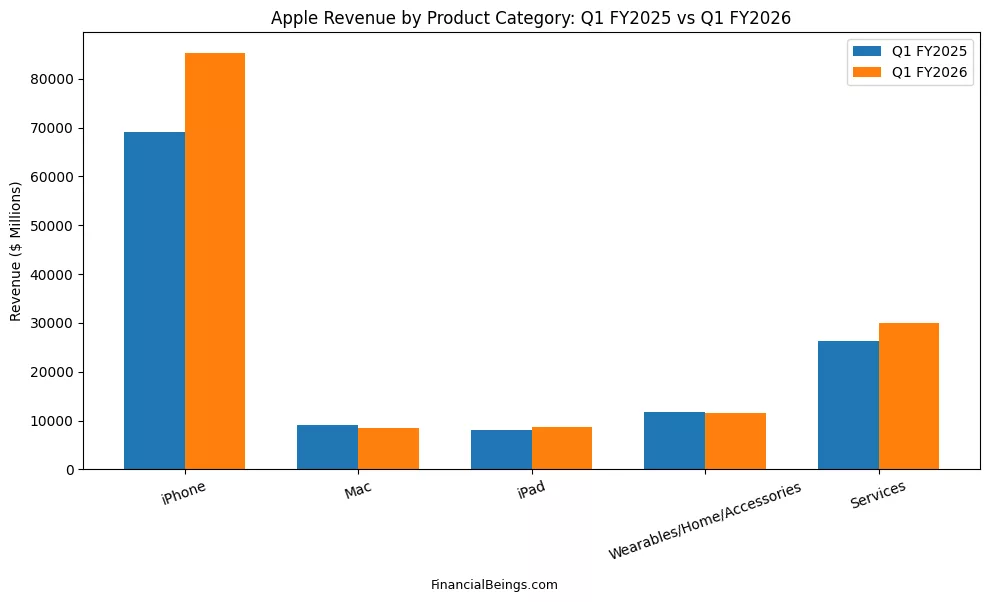
Table 4: Revenue Comparison ($ Millions)
| Product Category | Q1 FY2025 | Q1 FY2026 |
| iPhone | 69,000 | 85,000 |
| Mac | 9,000 | 8,500 |
| iPad | 8,000 | 8,800 |
| Wearables/Home/Accessories | 11,500 | 11,200 |
| Services | 26,000 | 30,000 |
Apple by product category in terms of revenue to identify not only the level of revenue that the company is making, but also the area that is growing. The concept of revenue concentration is important as it will show that growth is either spread out or concentrated on a small number of segments.
This indicate that iPhone revenue was the fastest-growing year-over-year, while Services revenue grew in a meaningful way. Conversely, Mac income fell marginally, Wearables were fairly stable and iPad did not grow remarkably. This means that ultimately, Apple does not have a balanced revenue trend in all its business lines. Rather, the growth is focused on iPhone and Services.
Apple Intrinsic Value 2026: Growth Sensitivity
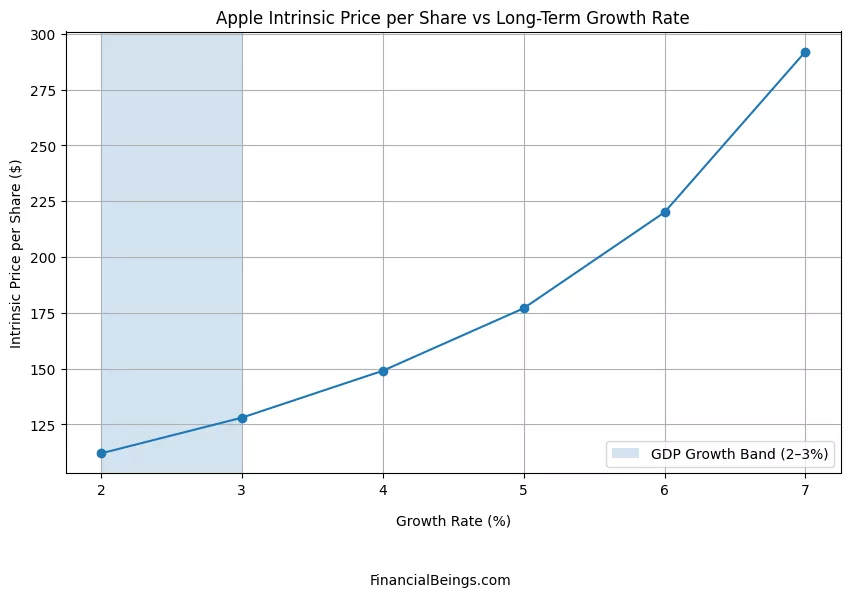
The intrinsic value analysis shows that long term growth assumptions are very sensitive to the valuation of Apple. Growth and intrinsic value relationship is not linear, it gets steeper as the projected expansion increases. To illustrate, an increment in intrinsic value is substantial when the growth rate shifts by 3% to 5% and a radical increase in valuation when the growth rate shifts by 3% to 7% percent. This implies that perceived fair value can be significantly induced by small shifts in the expectations of the investors. This sensitivity causes Apple stock to be very reliant on future estimations as opposed to past performance.
Hence, in 2026 intrinsic value, it is not the current revenue strength that has to be put in focus but sustainable growth that is not low-single-digit and economic growth can be maintained over a period of time.
Is Apple Stock Overvalued or Undervalued?
To find out whether the stock of Apple is overvalued or underestimated, it is necessary to match the expectations of the market with the realistic growth projections. In case long-term growth is stabilized in the range of conservative 2-3%, the valuation is considered overstretched when compared with intrinsic estimates. Nevertheless, in case Apple continues to grow at the 4-5% range, especially with the help of the Services monetization and the ecosystem development, the valuation can be justified reasonably. The expectation of higher growth rates (6-7%) suggests great confidence in the monetization of AI and long-term pricing power. The controversy is thus conditional as opposed to absolute.
Apple is currently priced as a high growth company as the price offers minimal margin of safety. The current price is highly sensitive to future growth developments with only 3% of the current price supported by current performance.
Is Apple Stock a Value Trap?
A value trap is where the company seems to be financially strong and unable to provide the growth that investors are hoping to receive, and then its returns will start to stagnate or fall. To get Apple in this category, the growth of Services would have to slow down significantly, hardware upgrade cycles would have to become less robust, and AI integration would have to be demonetised. The structural deterioration is not in revenue information at the moment (Yahoo Finance, 2026; Financial Times, 2026). Nonetheless, due to the concentration of growth of Apple in key areas, a sustained performance is necessary.
Immediate risk is eliminated due to the company ecosystem strength, but long-term value will rely on the ongoing innovation that will result in the growth that can be measured in financial terms.
Final Conclusion: Is Apple Stock Worth Buying?
Therefore, is Apple stock worth buying in 2026 following the growth of AI and Services?
This is based on the sustainability of long-term growth. If Apple is able to sustain 5-6% growth rate with the help of Services monetisation and successful integration of AI, the present-day levels of valuation will seem fair and potentially provide a mid-range increase. But at the same time, when growth becomes 2-3%, the potential to grow becomes quite restrictive. Where market expectations are already showing aggressive 6.5% long-term growth, the risk of valuation is significant.
Apple is a strong company that is financially diversified globally and reinforced by a robust ecosystem (Yahoo Finance, 2026; Financial Times, 2026). However, forward growth assumptions are very sensitive to intrinsic value. To the apple stock long-term investors who see apple’s growth imminent and are disciplined, Apple can still remain a good core allocation. Investors who are valuing long-term high growth with no room to spare should be cautious.
Ultimately, it does not matter whether Apple has a successful track record in the past, but its future products and initiatives must justify higher growth to provide higher returns to the shareholders. We explore how Apple’s innovation pipeline and strategic roadmap may shape that future in our forward-looking outlook, “forward-looking outlook“.
All calculations and valuation estimates are FinancialBeings’ own, based on data sourced from SEC filings AAPL (10K and 10Q), use or reproduction before prior approval is prohibited.
Should Investors Buy AAPL: FAQs
Is Apple a good stock to buy?
Apple is a good stock to purchase in the long run if long-term growth is sustained at 4-6%. According to the intrinsic value analysis, the moderate growth indicates that it has a reasonable valuation with opportunities for increased value. However, if growth is declining between 2-3%, then there is not much to gain, and projections can turn out to be too high. Thus, Apple is enticing to serious investors who think that Apple’s services revenue growth and AI integration are able to maintain high future growth trajectory.
Where will Apple stock be in 5 years?
According to the results of intrinsic value sensitivity, the sustainability of growth is the key to Apple’s position in five years. In case the company continues to have 5-6% long-term growth, valuation forecasts indicate the price per share of $260 to $320. When growth is compressed at a level of 2-3%, then price appreciation is restricted and we arrive at between $180-$200 per share. The five-year outlook has been attached directly to the capability of Apple to continue growing revenue steadily, as opposed to relying on its previous success.
How could Apple’s AI strategy impact it’s stock over the long term?
Apple’s AI strategy’s impact on stock has the potential to significantly affect the share price if it translates into a quantifiable revenue increase. If AI can expedite device upgrades, focus on premium pricing, and grow recurring subscriptions to Services, maintaining 5-6% long-term growth will be more feasible, which enhances intrinsic value. Nonetheless, if AI will render competitiveness but not grow monetization, growth can stagnate, which constrains valuation. The long-term effect of AI on the stocks should be that AI will become a source of revenue instead of a mere fairytale.
Usama Ali
Usama Ali is the founder of Financial Beings and a self-taught investor who blends classic valuation study with insights from psychology. Inspired by works from Benjamin Graham, Aswath Damodaran, Stephen Penman, Daniel Kahneman, and Morgan Housel, he shares independent, data-driven research to help readers connect money, mind, and happiness.
Disclaimer
The content provided herein is for informational purposes only and should not be construed as financial, investment, or other professional advice. It does not constitute a recommendation or an offer to buy or sell any financial instruments. The company accepts no responsibility for any loss or damage incurred as a result of reliance on the information provided. We strongly encourage consulting with a qualified financial advisor before making any investment decisions.