Apple stock forecast 2030 valuation based analysis. Analyse intrinsic value, projected returns analysis, growth assumptions analysis, and over- or under-pricing of AAPL for long-term investors.
Introduction
Apple Inc. is considered one of the strongest and most profitable companies in the world’s equity markets. However, the connection between the intrinsic value and the market price is not the only determinant that adds to the long-term shareholders’ returns, which also relies on the excellence of its operations. Apple stock price vs intrinsic value evaluates the potential of Apple’s current stock valuations to be underpinned by the operating fundamentals and realistic growth outlook by 2030.
This article not only relies on the narrative predictions but also on a valuation-based model, which is founded upon the sensitivity of intrinsic value, residual income drivers, Net Operating Assets (NOA), Operating Liability Leverage (OLLEV), and Return on Net Operating Assets (RNOA). Financial data interpretation also depends on the official disclosure of financial information of Apple, and it renders it transparent and reliable (Apple Inc., 2024a).
Apple Stock Forecast 2030 Valuation-Based Analysis
According to this Apple Stock long-term valuation, it is evident that Apple is still a quality business, but long-term, an investment will be extremely valuation-based. The current market price of Apple assumes a long-term growth rate that is much higher than the global GDP rates, depending on the sensitivity of the intrinsic value, the trend of operating performance, and the underlying residual income.
- According to the more conservative growth projections (2-3 per cent), Apple intrinsic value 2030 is projected to be lower than the prevailing value in the market, and therefore it does not present a high degree of margin of safety.
- Market-implied growth (around 7%): At the market-implied growth, the intrinsic value is the current price, implying that the company is not overvalued but optimistically fairly valued.
- High RNOA, high operating leverage, and efficiency of capital of Apple are also factors that can maintain the business of Apple in the long run, but cannot exclude the valuation risk.
Investment signal:
Apple is not a deep-value Buy, but a Hold, at the present valuation, to long-term investors. If APPL can continue the long-term currently market implied growth rate of 7.1%, the projected price in 2030 would be $414 per share with an expected return of 10.26% per annum. Though the 7.1% market implied growth rate is high.
Valuation Framework and Data Sources
In this discussion of Apple valuation model assumption, Apple residual income valuation would be followed, in which the derivation of the shareholder value would be pegged on:
1. Sustainability and the quantity of operating returns (RNOA).
2. Scale and efficiency turnover (NOA).
3. Application of operating liabilities as a leverage mechanism (OLLEV).
4. The market prices hold long-term growth expectations.
Intrinsic Value Sensitivity and Long-Term Growth Assumptions
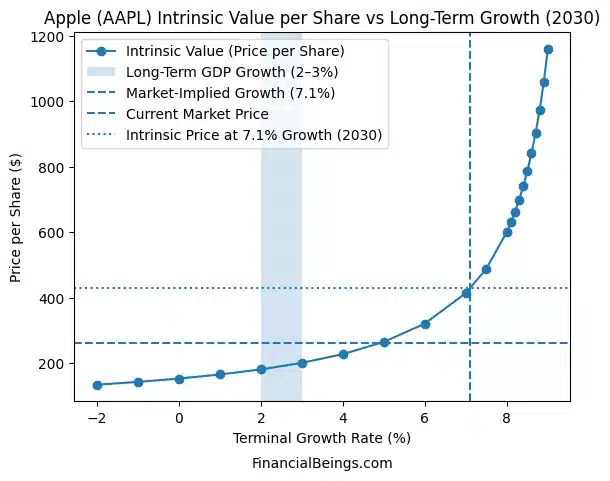
Figure 1. Apple (AAPL) intrinsic value per share versus long-term terminal growth assumptions (2030)
This indicates that the estimated intrinsic value of Apple reacts to a range of growth in the long-term perspective, Apple valuation analysis is sensitive to the growth forecasts and the predictability of the market-implied growth with the current value of shares. We have re-evaluated AAPL after the AI services agreements with other companies, read our 2026 Apple stock analysis, “Is Apple Stock Worth Buying in 2026 After AI and Services Growth—Or Is It a Trap?”
The intrinsic value sensitivity reveals that there is a non-linear relationship between the long-term growth assumptions and the intrinsic value of Apple per share. The intrinsic value estimates are below the current market values at growth rates that are equal in line with the long-term economic growth (around 2-3 per cent), a fact that implies that valuation support becomes very low in cases of conservatism.
The intrinsic value curve, on the other hand, is high when the growth is high, and the intrinsic value limits the existing market price when the growth assumptions shift towards the market-implied growth of approximately 7%. This means that there is a current valuation pegged on optimistic yet not over-optimistic growth of Apple in future.
The question which will be answered with the help of this finding is: Is Apple stock overvalued in 2030? Apple does not appear to be structurally overvalued based on the valuation mechanism, but its stock price ought to be capable of supporting more than GDP growth to support existing prices (Apple Inc., 2024a).
Net Operating Assets (NOA) and Reinvestment Dynamics
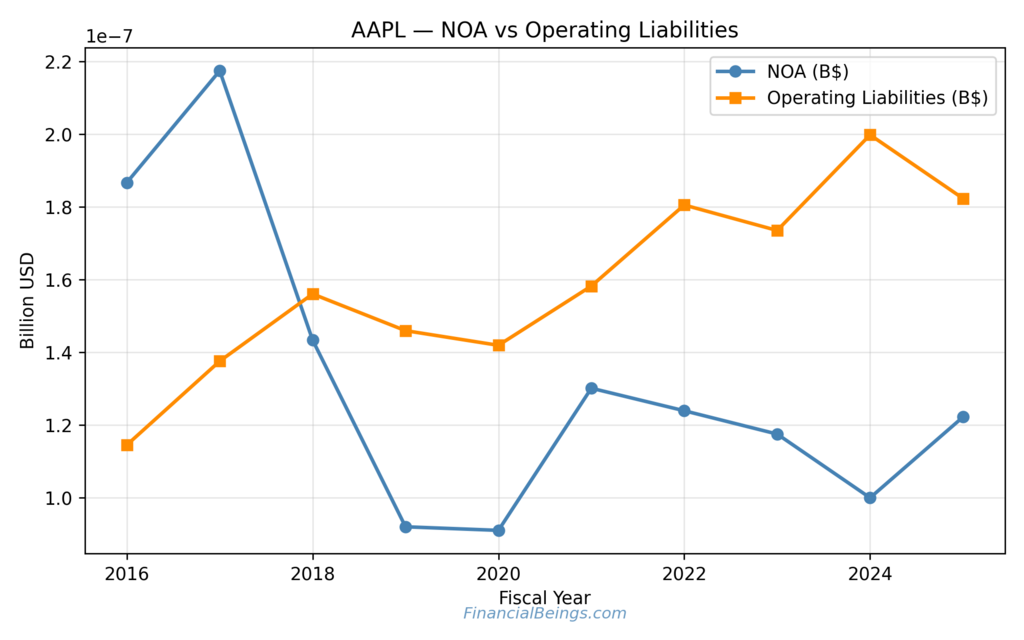
Figure 2. Apple (AAPL) net operating assets and operating liabilities over time.
Operating Liability Leverage (OLLEV) and Risk Implications
This represents net operating assets and operating liabilities of Apple, which shows the trends in capital reinvestment and the way in which the operating liabilities were used to fund the business operations.
Net Operating Assets show the capital that Apple spends on its operations. The trend of the NOA demonstrates intervals of capital efficiency improvement with the new reinvestment cycles. Such swings suggest that Apple can balance its cash generation, reinvestment and balance sheet optimization strategies (Apple Inc., 2024b).
They have gone structurally over time based on the operating liabilities, which implies that Apple has been enjoying the benefits of financing part of operations as a result of non-interest-bearing sources such as supplier obligations and deferred revenue. The structure enables the creation of residual income as well as helping in sustaining high operating returns.
It further, though, implies that the further increase of NOA with time will require further vital capital that may absorb the long-term increase in valuation in case the returns to new investments become normal.
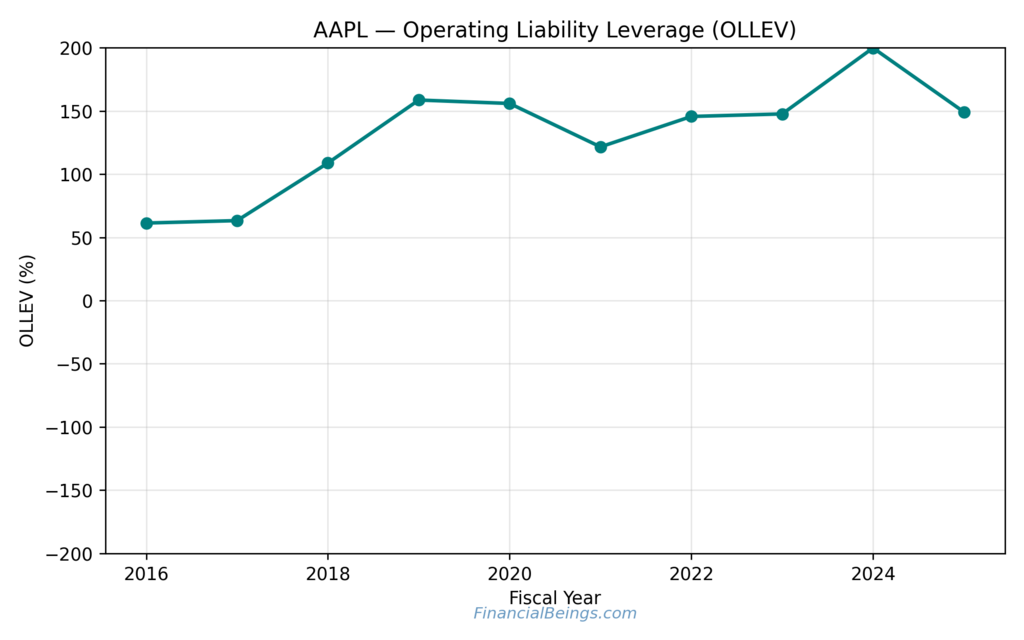
Figure 3. Apple (AAPL) operating liability leverage (OLLEV) trend.
This value shows the trend of Apple’s operating leverage of liability, which has been increasing based on the effect of operating liabilities that have been increasing operating returns, as well as valuation that is sensitive to growth and margin changes.
Operating Leverage (OLLEV) is applied to find how effective operating liabilities are to maximize returns on operating assets. The OLLEV trend in Apple is quite high, which contributes to the ability of the company to market the RNOA on the basis of operational financing, rather than traditional debt.
Though this leverage makes profitability better in the periods of incessant growth, it also increases the vulnerability of valuation to the losses in revenue growth or margin growth. Regarding Apple’s residual income valuation, the high OLLEV can only contribute to value creation when the performance in the operation is healthy (Apple Inc., 2024a).
Thus, OLLEV is a value-additive as well as a risk-additive in the future operating conditions.
Return on Net Operating Assets (RNOA): Core Value Driver
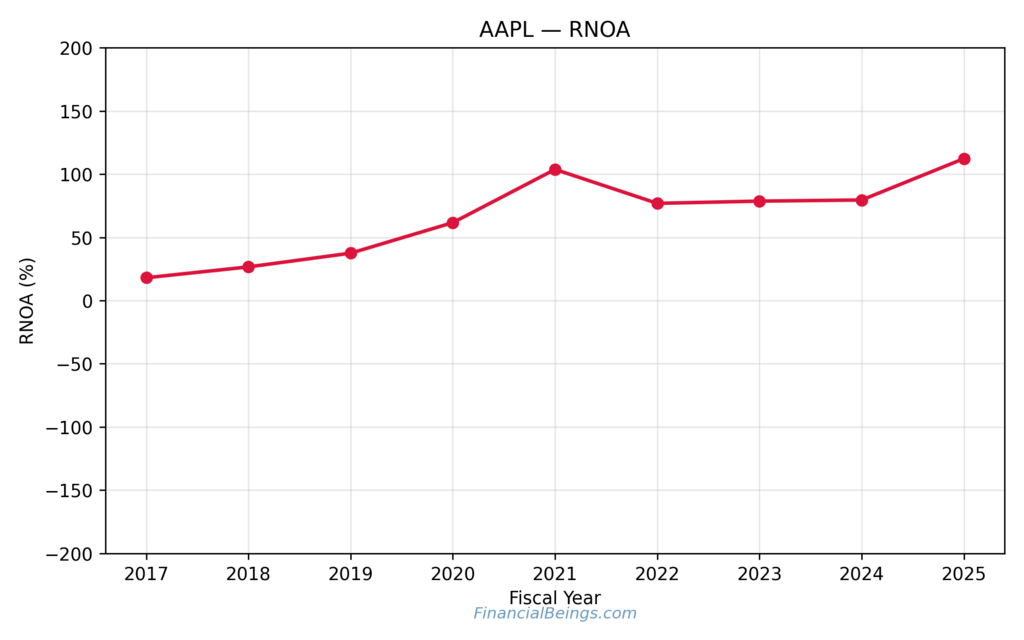
Figure 4. Apple (AAPL) return on net operating assets (RNOA)
This figure gives the trend of the Apple ROA that indicates the ability of the company to achieve high operating returns on the expended operating capital and its importance in the valuation of the residual income.
RNOA is the fundamental source of residual income and intrinsic value. Apple has a strong and steady operating profitability trend that speaks of brand power, pricing discipline, and ecosystems benefits.
The RNOA moderation to the highest levels is explained, but the structural levels of RNOA are high, which proves the point that Apple still generates returns that are much higher than the operating cost base. This enables the power of the company to maintain an intrinsic value even at the lower growth stages (Apple Inc., 2024b).
Valuation theory, however, notes that high returns in their own right not sufficing to guarantee higher shareholder returns when it is already the case that the expectation of growth was already incorporated into the stock price.
Expected Returns and Valuation Implications Through 2030
Apple expected return forecast points towards the fact that the future shareholder returns are likely to be driven by earnings stability and cash dividends rather than numerous growth factors. Growth in intrinsic values appears to be relatively small, and the long-term returns would be medium to low in the more conservative growth conditions.
Provided that Apple can sustain growth better in line with market-implied expectations, intrinsic value can justify current levels of pricing. However, the analysis shows that there is not much asymmetry: there is a chance to increase but little, but there is a high probability in the case that the growth expectations will not be met.
In this respect, the Apple long-term stock valuation is not underestimated but appears to be acceptable and fragile.
Portfolio Implications by Investor Profile
The risk of valuation at Apple may be perceived differently by the diversity of the investors, depending on their goals and risk-taking capacity. The ways that Apple (at its current values) can be included in various portfolio strategies are below:
Growth Portfolios
AAPL can also be added to a growth-oriented portfolio where the investors would focus on growth. Apple is reputed to have a track record of innovation and an increase in profits, and risk-takers who may desire to expand can perhaps risk betting on it going higher. However, they must remember that to a large degree, the growth is already priced in, and this can constrain future returns. Apple can also be included in the core holdings in a growth portfolio due to the quality, but it needs to be position-sized due to the high valuation risk.
Balanced Portfolios
Selective Investment in Apple may be undertaken by people with balanced or blended portfolios, though they must understand the risks of valuation. A balanced portfolio manager may own Apple because it is stable, liquid, and the leader in its industry, but hedge or limit its ownership. One Stock is a better buy than AAPL for balanced portfolio, find it here.
In essence, long-term but lower returns would be available to balanced investors to hold on to Apple. They should be prepared for the eventuality of several expansions being constrained (or even worse, reduced) in the event of Apple not doing as well as the growth forecasts. It is wise to be observant, and others can wait to achieve a better point of entry and then make significant additions to positions.
Conservative Portfolios
It will not be a place that defensive or value-oriented investors will run to at this stage with Apple. In the conservative view, the margin of safety and protection against downside risk is not and is a great disincentive. These investors are more interested in the preservation of the capital, and they usually pursue the stocks which are trading at a low price as compared to the intrinsic value. Apple, at its present trade position of having well exceeded most of the fair value assumptions in a reasonable growth scenario, does not give a valuation cushion desirable to a conservative investor.
The conservative portfolios will most likely lie on the sidelines unless the price turns or the fundamental factors turn in the positive direction as compared to the expectations. In conclusion, neither value nor risk-averse investors would find their risk/reward profile of Apple at its present price to be meeting their high-standard criterion and would want to avoid Apple in this case rather than risk over-paying.
Long-term Apple stock investment outlook: Buy, Hold, or Avoid?
This is because the Apple Stock Forecast 2030 Valuation-Based Analysis believes that the future of Apple is not as bright as its financial health. Apple is also a quality and a strong firm as regards to financial stability, so a Buy rating among investors who would be interested in long-term stability and survival of business, instead of the growth of price in the short run.
A Hold position is appropriate to the current shareholders. The long-term growth already is being factored into the existing market prices, and one can assume that future returns are going to be stable but moderate and terminated by earnings sustainability, unlike valuation growth.
Apple is, however an Avoid to the value-oriented investors at such levels. The intrinsic value estimates under conservative growth assumptions have a low margin of safety, which implies that Apple is not a low-valuation strategy business but a safe business.
Conclusion
The operating fundamentals of Apple are also quite good and have been facilitated by high RNOA, high operating leverage and tight capital management. However, according to the AAPL valuation analysis, the present stock price of Apple reflects excessive estimates of long-term growth.
The Apple Stock Forecast 2030 Valuation-Based Analysis concludes that Apple is a quality hold, and it is a stable company with and predictable cash flow giving company, rather than overvalued returns. Investors are therefore expected to be on par with valuation reality as compared to business strength.
All calculations and valuation estimates are FinancialBeings’ own, based on data sourced from SEC filings AAPL (10K and 10Q) use or reproduction before prior approval is prohibited.
Usama Ali
Usama Ali is the founder of Financial Beings and a self-taught investor who blends classic valuation study with insights from psychology. Inspired by works from Benjamin Graham, Aswath Damodaran, Stephen Penman, Daniel Kahneman, and Morgan Housel, he shares independent, data-driven research to help readers connect money, mind, and happiness.
Disclaimer
The content provided herein is for informational purposes only and should not be construed as financial, investment, or other professional advice. It does not constitute a recommendation or an offer to buy or sell any financial instruments. The company accepts no responsibility for any loss or damage incurred as a result of reliance on the information provided. We strongly encourage consulting with a qualified financial advisor before making any investment decisions.